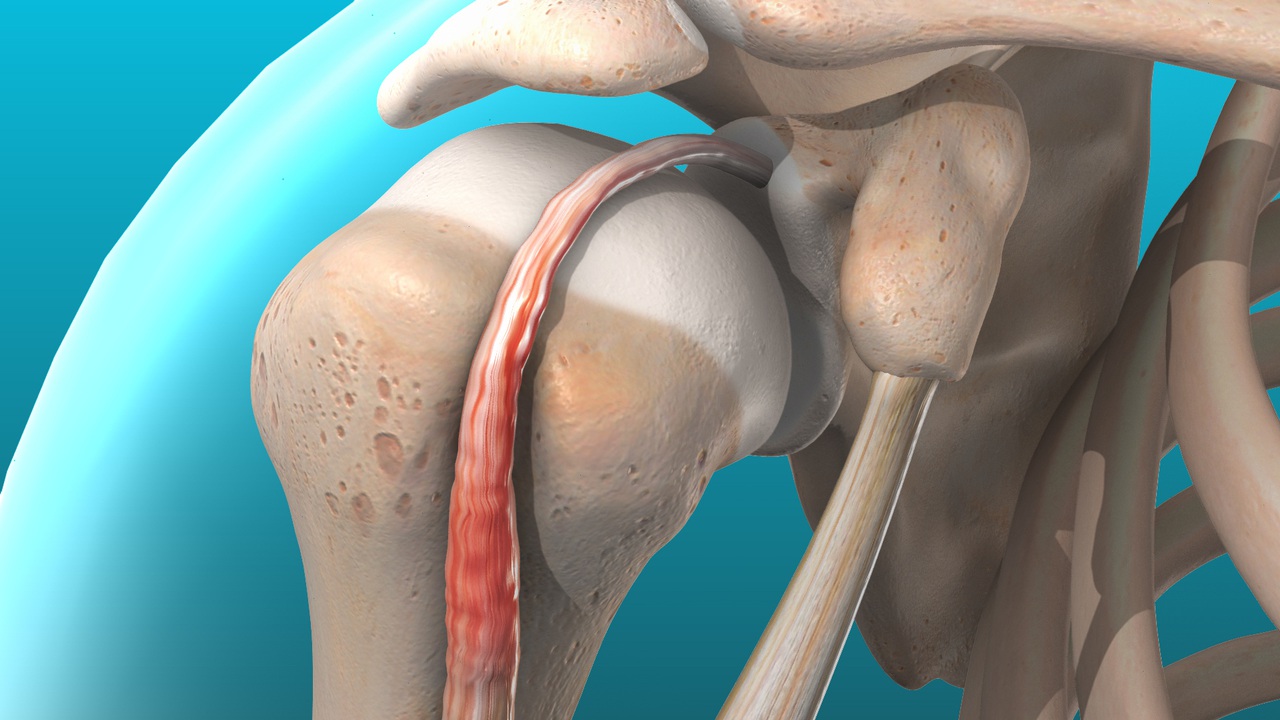
Tendinitis is the inflammation of a tendon, the thick fibrous cord that connects muscle to bone. It usually develops due to repetitive movement, overuse, or sudden injury. This condition is particularly common in individuals who play sports, perform physical labor, or engage in repetitive activities. Areas like the shoulder, elbow, wrist, knee, and heel are often affected. The pain associated with tendinitis usually worsens with movement and may feel sharp or achy. Swelling, tenderness, and a feeling of tightness around the joint are also common.
What Is Bursitis?
Bursitis is the inflammation of the bursa, a small fluid-filled sac that cushions bones, muscles, and tendons. When irritated, the bursa can swell and cause pain, particularly during movement or pressure. Common locations for bursitis include the shoulder, elbow, hip, and knee. It can occur as a result of repetitive movement, trauma, infection, or chronic pressure. Unlike tendinitis, bursitis often causes more noticeable swelling and may present with warmth or redness over the joint. The pain can be constant and may persist even when the joint is not being used.
Key Differences Between Tendinitis and Bursitis
While both conditions lead to joint pain and limited mobility, the primary difference lies in what is inflamed. Tendinitis affects the tendon, whereas bursitis involves the bursa. Tendinitis pain is usually triggered by specific movements, while bursitis pain is more generalized and can even be felt at rest. Bursitis often causes visible swelling, which is less common in tendinitis. Recognizing these differences is critical in determining the correct diagnosis and treatment.
The Importance of Comprehensive Orthopaedic Care
Effective diagnosis and treatment require a thorough approach. Comprehensive orthopaedic care includes a detailed medical history, physical examination, and advanced imaging techniques like MRI or ultrasound. Orthopaedic specialists use this information to distinguish between similar conditions and rule out other causes like arthritis, nerve compression, or structural damage. This holistic approach ensures the patient receives the right care based on an accurate diagnosis.
Treatment Options and Recovery
Both tendinitis and bursitis are typically managed with non-surgical methods at first. Rest, ice, and anti-inflammatory medications help reduce swelling and pain. Physical therapy can play a significant role in strengthening surrounding muscles, improving flexibility, and preventing recurrence. In more severe or persistent cases, corticosteroid injections may be used to reduce inflammation. Surgery is rarely needed, but may be considered if conservative treatments fail. Early intervention through a comprehensive orthopaedic care plan can lead to faster recovery and minimize the risk of chronic pain or joint damage.
Long-Term Management and Prevention
Preventing future episodes of tendinitis or bursitis involves understanding the triggers and modifying activities that place stress on the joints. A comprehensive orthopaedic team often provides education on ergonomics, posture, exercise, and stretching routines. Whether you’re an athlete or an office worker, taking proactive steps can reduce your risk.
Conclusion
Tendinitis and bursitis may seem similar, but recognizing their unique symptoms is essential for proper treatment. Through comprehensive orthopaedic care, patients can receive a precise diagnosis and personalized treatment plan. This not only alleviates current symptoms but also promotes long-term joint health and function. Seeking expert care early can make a significant difference in recovery and overall quality of life.